Network
- Why 255/0 is not used in IPv4 address? 255 is used for broadcast, and 0 is used by device when booted and before receiving assigned IP address.
- In the four TCP/IP layer structure, there are link (hardware), network (i.e. IP), transport (i.e. TCP) and application (logic representation) layers.
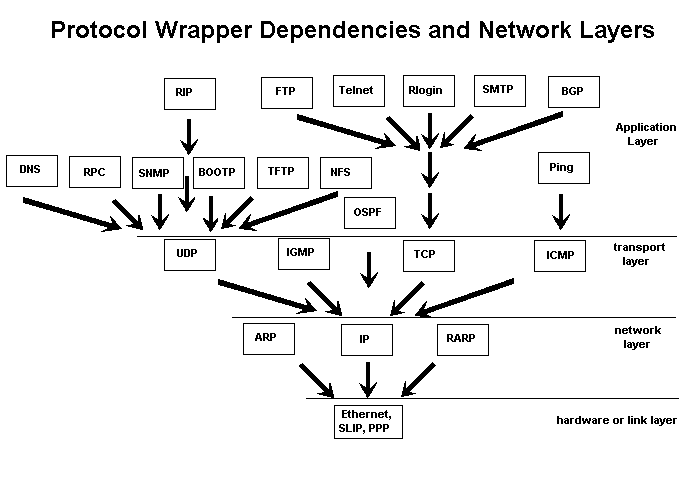
Four TCP/IP layer.
- OSI layer: Physical -> Data link -> Network -> Transport -> Session -> Presentation -> Application.
- IP: Internet Protocol (IP) is at network layer, which provides addressing, security (encapsulation), type of service, fragmentation and re-assembly. But it does not guarantee order or integrity.
- TCP: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is at transport layer. It provides end-to-end reliability, sequencing of packets and flow control.
- CSMA: mainly used when there can be jam of traffic in network channel, especially wireless network. CSMA/CA is collision avoidance (CA) version, which tries to avoid collision; CSMA/CD is collision detection (CD) version, which terminate transmission once collision is detected, and thus improving performance of CSMA by shortening retry time.
Security
- HTTPS process: client request secure session -> server responds with certificate (with public key on that) -> client encrypt the session key with public key -> server decrypt the session key -> the rest of the session will use the session key. Roughly speaking, it is on session layer of OSI layer.
- Kerberos: a MIT-developed network authentication protocol. The basic process is:
- User logins in client interface, and client logins with user info to Authentication Service (AS)
- AS checks user identity, replies back with Ticket to Get Ticket (TGT)
- Client uses TGT to request service on Ticket Granting Service (TGS)
- TGS checks TGT and replies with Service Ticket
- Client uses Service Ticket to request service on service provider device
- Advantages of proxy server:
- hide inner IP topology
- can act as a firewall
- add an abstraction layer (on application, serucity and so on)
- RSA encryption
- choose prime number p, q
- n = pq
- choose a e that is not a divisor of (p - 1)(q - 1)
- find d such that (de)mod(p - 1)(q - 1) = 1
- then public key is e,n, private key is d
- ciphertext c=m^e mod n, message m=c^d mod n
- Security in Android app:
- permission: Before installing app, it will prompt user for permission.
- local data: When using internal storage, we can edit flags to make it unaccessible for other applications. When using external storage, we can perform input validation. When using contentProvider, which can be accessed for other applications, and can modify the accessibility in read and write.
- network data: We should always try to use HTTPS or SSL protocol when using network data.
- user data storage: Using accountManager to store password, or KeyStore for storage.
- dynamically loading code: Don’t load code that is not in your application SDK (especially the unencrypted internet data). That’s one of the reason why we need to register activity on manifest.xml.
- WebView: Caution when loading JavaScript code. And they are granted the same permission as your application.